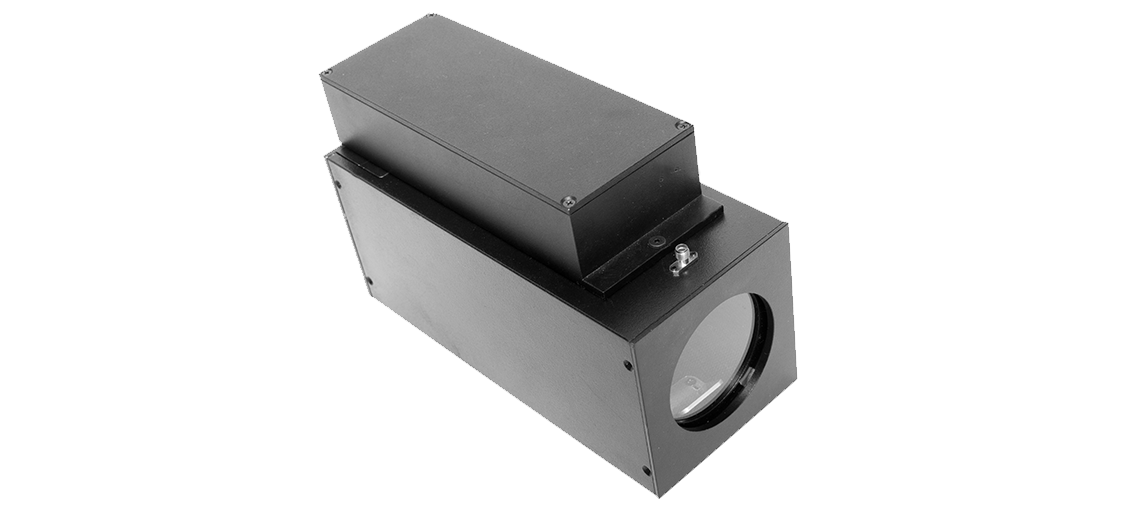
The Xenon Illuminator is highly versatile and widely used across various fields of scientific research due to its broad-spectrum light emission, which closely mimics natural sunlight. Its applications extend across disciplines such as biology, chemistry, physics, and materials science.
The appliance is typically equipped with an elliptic reflector which generates a white light beam converging into a single focal point about 20 cm from the lamp output window. This way one can vary light intensity density by changing sample distance from the housing.
Due to an reflector engulfing the lamp, the setup has very good efficiency. Up to 70% of emitted radiation is captured by the reflector and directed at an illuminated sample.
As optional features, the unit may provide three types of stabilization:
- electric current,
- electric power,
- light intensity stabilization.
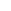
The light intensity stabilization mode helps the long term (order of hours) stability of the output beam. It also reduces the warm up time to about 3 minutes as compared with 30 minutes or longer in the current stabilization mode.
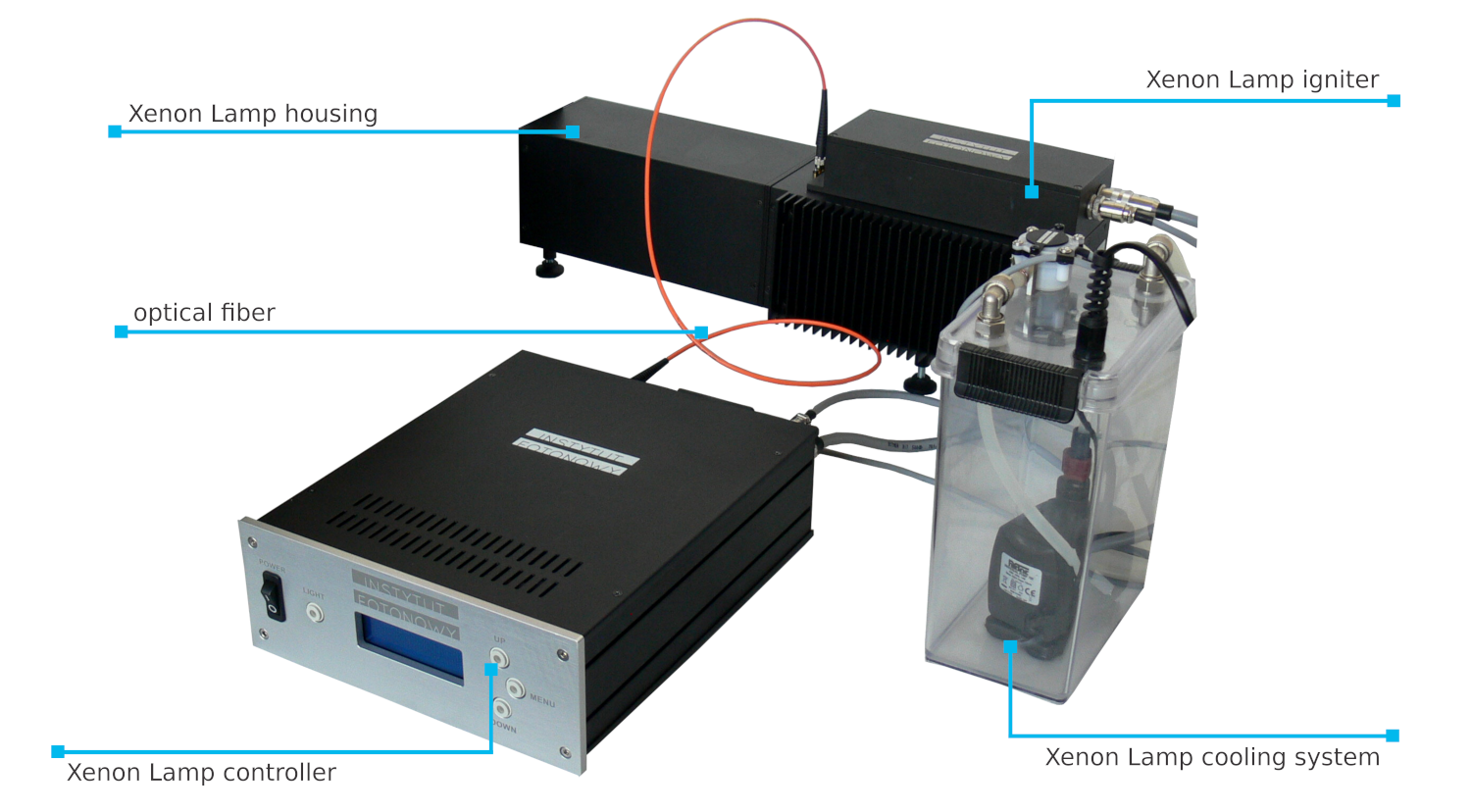
- Xenon Lamp housing.
- Xenon Lamp igniter.
- Xenon Lamp controller.
- Xenon Lamp cooling system.
- Optical fiber.
- Nominal electric power: 150 W
- Output beam: horizontal or vertical
- Reflector type: elliptical (for convergent beam)
or parabolic (for collimated beam) - Reflecting system efficiency: up to 70 %
- Maximal electric current: 8.5 A
- Normal working current: 7.5 A
- Current resolution: 0.1 A
- Stabilization of current: better than 0.1 %
- Stabilization of light intensity: available
- Warm up time: less than 180 sec (in light stabilization mode)
- Current monitor output: BNC.
- Photodiode monitor output: BNC.
- Counter of bulb’s working hours .
- Low electromagnetic emissivity of lamp starter,
safe for other devices. - Quiet water cooling system.
- Voltage: 230 V, 50 Hz.
- Optical bench: optional
The plot shows the difference in light intensity evolution in two available stabilization modes. The current in the current stabilization regime is kept constant with about 0.0025 % accuracy. Despite
of that, the light intensity changes significantly over time (black line) due to temperature and pressure changes within the xenon bulb.
The light intensity stabilization eliminates the long term drift
in the light output and makes it stable just 3 minutes after the lamp is switched on.